Aboveground biomass rate (AGBd, kg m-2 d-1) is calculated on a daily time step as:
![]()
where Rad (MJ m-2 d-1) is daily global solar radiation, ![]() is the fraction of PAR absorbed by the canopy, k is light extinction coefficient, LAI (m2 m-2) is green leaf area index (total leaf area index is used to compute the fraction of PAR intercepted by the canopy), RUEact (g MJ-1) is actual photosynthetically active radiation (PAR=0.5·Rad, MJ m-2 d-1) use efficiency, which varies according to irradiance level, CO2 concentration, development stage, diseases, nitrogen concentration and thermal limitations. In the current version of the model, it is calculated as follows:
is the fraction of PAR absorbed by the canopy, k is light extinction coefficient, LAI (m2 m-2) is green leaf area index (total leaf area index is used to compute the fraction of PAR intercepted by the canopy), RUEact (g MJ-1) is actual photosynthetically active radiation (PAR=0.5·Rad, MJ m-2 d-1) use efficiency, which varies according to irradiance level, CO2 concentration, development stage, diseases, nitrogen concentration and thermal limitations. In the current version of the model, it is calculated as follows:

![]()
RUEmax (kg MJ-1) is the RUE value (crop parameter) not limited by water, nutrients, pest, diseases, senescence, excess of radiation, temperature, damages. Tlim, Rad_F and DVS_F are unitless factors in the range 0 (maximum stress) – 1 (no limitation) accounting for temperature limitations, saturation of the enzymatic chains, and senescence phenomena, respectively. CO2_F (unitless) account for the effect of CO2 concentration on RUE.
Tlim is the temperature-limitation factor, calculated according to Yan and Hunt (1999):

where T (ºC) is the mean daily air temperature, Tc (ºC) is the ceiling air temperature at which crop growth ceases, To (ºC) is the optimal air temperature at which the maximum rate of development occurs, Tb (ºC) is the base air temperature for crop growth, C is a shape factor set equal to 1.8 to allow the beta-function to approximately cross linear progression between Tb and To at Tlim=0.5 (see figure below as an example with Tb=0, To=30, Tc=40).

The factors accounting for saturation of the enzymatic chains involved with photosynthesis (Rad_F) and for the effect of senescence (DVS_F) are calculated using empirical functions derived, respectively, by Choudhury (2001) and Campbell et al. (2001):
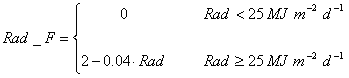

where DVS is the development stage code.
The factor accounting for CO2 effect on RUE is calculated according to the approach proposed by Stockle et al. (1992), empirically derived by measurements carried out in growth chambers with different levels of CO2 concentration:

where [CO2] is atmospheric CO2 concentration (the equation is valid for C3 species).
Algorithms to account for other factors on RUE are under development.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Free iPhone documentation generator