Great attention was paid in respecting the granularity of the modelling approaches implemented, aiming at enhancing the reusability of the models for specific applications. Models are implemented in the Diseases components as simple, context and composite strategies, which represent the translation of the conceptual design patterns. The criteria followed to define a simple strategy and to aggregate simple strategies in context and composite strategies are illustrated in the figure below:
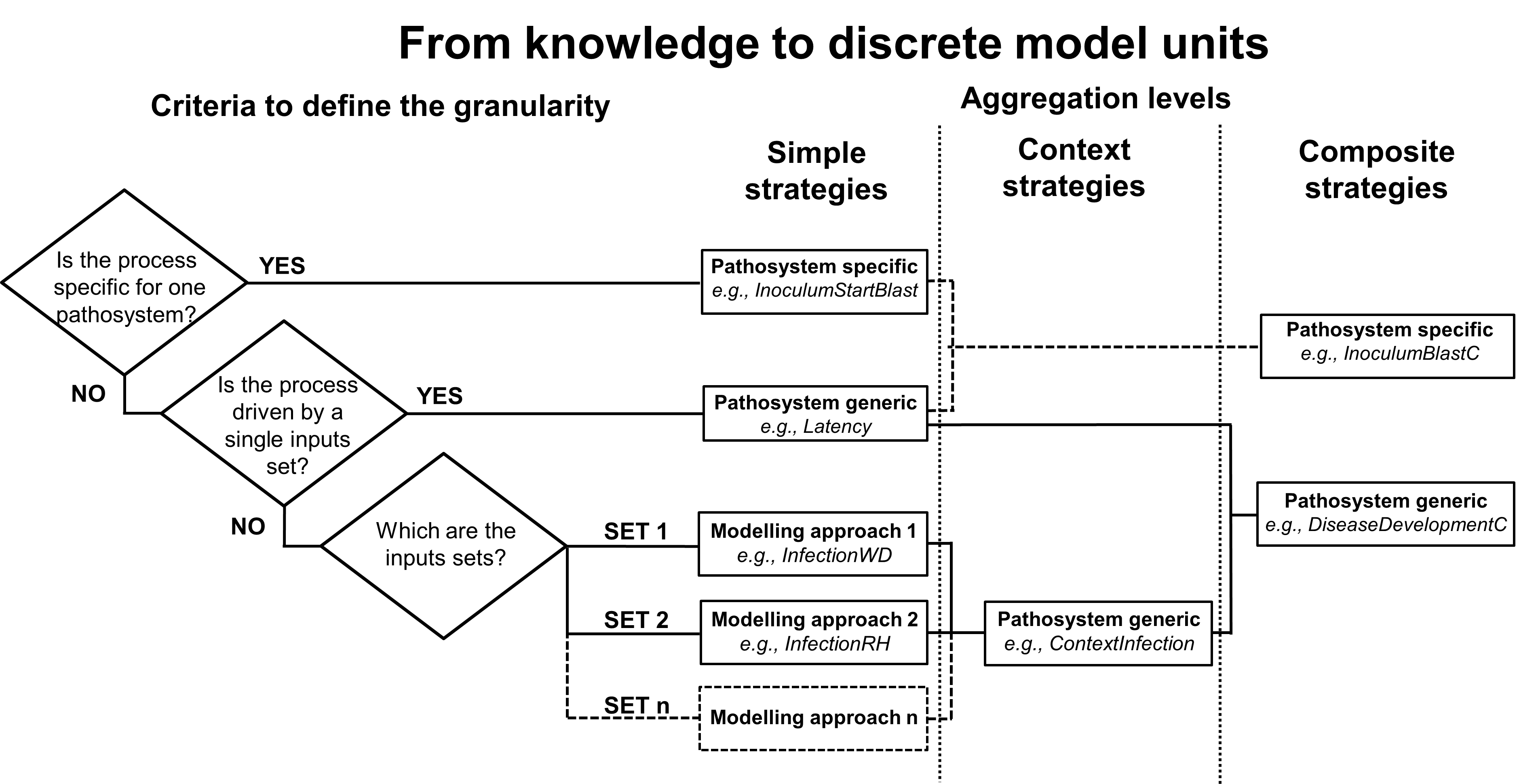
Criteria followed for the definition of simple strategies (left part) and aggregation of simple strategies into context and composite strategies (right part). Examples of strategies implemented in the Diseases components are provided at each aggregation level.
If a model is developed for a specific process of a given pathosystem, then a pathosystem-specific simple strategy has to be defined (first criterion).
If not, the second criterion allows to switch between process models that depends upon a single set of inputs (pathosystem-generic simple strategy) and processes driven by different input sets (simple strategy for a group of pathosystems).
In the latter case, the third criterion determines the definition of a number of simple strategies equal to the number of the different input sets. The aggregation of these simple strategies lead to the definition of context strategies, which contain the logic to switch between the different inputs sets, according to the pathosystem to be simulated. The definition of composite strategies can be done at different levels.
Pathosystem-specific simple strategies can be aggregated to simple, context and composite strategies, leading to pathosystem-specific composite strategies. The aggregation of pathosystem-generic simple and context strategies leads to pathosystem-generic composite strategies. All the strategies implemented in the Diseases components are presented in Table 1, with their inputs, outputs and parameters.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Free iPhone documentation generator