The length of the infectious period is defined as a function of air temperature only. Infectiousness is calculated according to a modified version of the method proposed by Blaise and Gessler (1992), in which the length of the period varies with temperature through a beta function (Yan and Hunt, 1993), as reported by Reed et al. (1976), as done for latency and incubation.
The temperature response function (f(t), 0-1) is computed with an hourly time step and it is defined as:
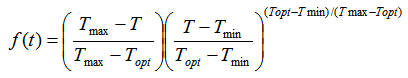
where T is hourly air temperature (°C), Tmin, Tmax and Topt are pathogen specific cardinal temperatures for the infectious period (°C).
In the hours when T is below Tmin or above Tmax, the percentage of host tissue affected by sporulating lesions does not further produce spores.
The duration of the infectious period (Infectiousness, days) is then computed as:

where Infnessmax is the maximum duration of the infectious period (i.e., the duration of the infectious period at optimum temperature, days).
The four parameters Tmin, Topt, Tmax and Infnessmax need to be determined for each simulated pathosystem.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Free HTML Help documentation generator