The model to simulate the infection process of fungal plant pathogens was formalized by Magarey et al. (2005). This model is operationally used by the NCSU-APHIS Plant Pest Forecasting system (NAPPFAST), and can be parameterized for 95 foliar fungal pathogens. This model is driven by temperature and leaf wetness or relative humidity.
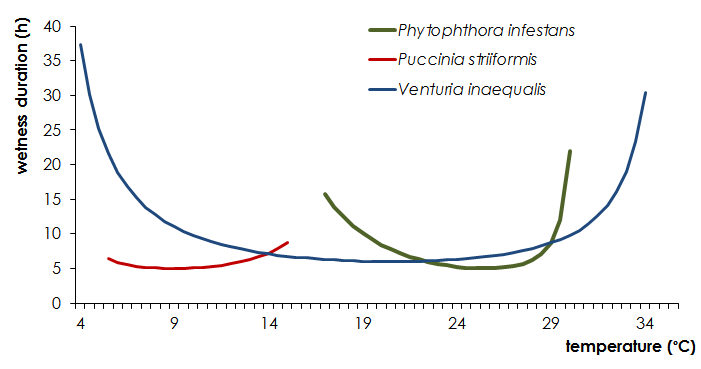
Wetness duration requirements computed by the Magarey et al. (2005) model
at different temperatures of the pathogens Phytophtora infestans, Puccinia striiformis and Venturia inaequalis.
Curves are plotted in the range of temperatures Tmin < T < Tmax.
This model has biologically meaningful parameters and takes into account the impact of both air temperature and leaf wetness duration by means of two functions. It implements the hourly air temperature response function developed by Yan and Hunt (1999):
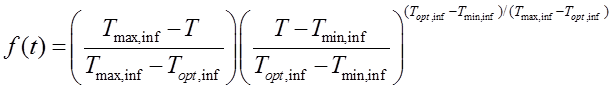
where f(t) (0–1; dimensionless) is the temperature response function; T (°C) is the mean air temperature during the wetness period; Tmin,inf, Tmax,inf and Topt,inf (°C) are the minimum, maximum and optimum temperatures for infection, respectively. The wetness duration requirement of the infection process is then computed based on the temperature response function, as:
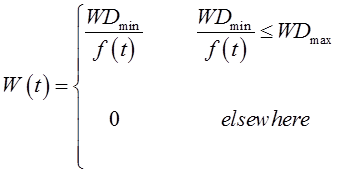
where W(t) (0–1; dimensionless) is the wetness response function, WDmin (h) is the minimum leaf wetness duration for infection, f(t) (0–1; dimensionless) is the temperature response function (Eq. (1)) and WDmax (h) is the optimum value of leaf wetness duration requirement. The impact of a dry period on infection fulfillment is determined by the critical dry period interruption value (D50), as indicated in the following equations:
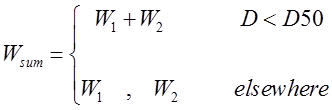
where Wsum is the sum of the leaf surface wetting and W1 and W2 are two wet periods separated by a dry period (D; h). According to this equation, if D > D50 then the model considers the two wet period as separated.
Alternatively to leaf wetness, the same model can be used with air relative humidity as the driving moisture source for pathogens which are not sensitive to wetness duration. In this case the parameter WDmin (h) is substituted with a minimum duration of relative humidity. The duration of suitable conditions to the fulfillment of an infection event is computed as the sum of hours above a pathogen specific relative humidity threshold.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Write eBooks for the Kindle