Pasting temperature is a RVA profile index, representing the temperature at which the starch viscosity starts to rise during heating process (Liang et al., 2003). Usually its value is higher than the gelatinization temperature, meaning the starch granules are completely gelatinized before the viscosity begins to rise.
The available modelling approach simulates the pasting temperature of rice as function of air temperature perceived by the crop during the whole ripening period. In particular this index is derived using a linear regression on the mean value of average air temperature occurring during the above mentioned phenological phase.
The general equation developed for Japonica varieties (Shen et al., 2007) is given below:
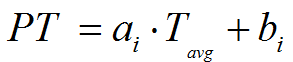
Where:
PT (°C) is the pasting temperature of rice starch;
Tavg (°C) is the average air temperature that occurs during the entire ripening of rice;
ai, bi (unitless) are the coefficients of the equation, specific for medium and long grain Japonica varieties.
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Generate EPub eBooks with ease