Daily minimum, maximum and average values of surface soil temperature are calculated by the equations developed by Parton (1984). Required inputs to the model are daily minimum and maximum air temperatures, plant biomass. Maximum soil surface temperature (Txs, °C) is predicted as a function of the maximum air temperature (Txa, °C) and the plant biomass; minimum soil surface temperature (Tns, °C) is a function of minimum air temperature (Tna, °C)and plant biomass. Soil surface temperature follows:
![]()
where Txa is the maximum air temperature (°C), B is the plant biomass (Kg m-2) and St is the daily solar radiation (MJ m-2) .
Parton (1984) showed that maximum soil surface temperature increases when air temperature increases up to 25 °C; then it approaches slowly a constant value. Increasing plant biomass is due to elevation of Txs over Txa decrease; plant biomass levels above 0.4 Kg m-2 cause the Txs to be lower than Txa.
Plant biomass adsorbs and reflects solar radiation reducing soil surface incident radiation amount. Plant biomass parameter values effect on maximum soil surface temperature varies for different plants; however, the equation general form is used (Parton, 1984). Maximum air temperature and total daily solar radiation are closely related to maximum soil surface temperature.
The minimum soil surface temperature is predicted as:
![]()
where Tna is the minimum air temperature (°C) and B is the plant biomass (Kg m-2). Minimum soil surface temperature increases when plant biomass increases; they are due to and long-wave radiation night losses decrease (Parton, 1984).
Daily average soil surface temperature is a weighted sum as following:
![]()
When day length is known:
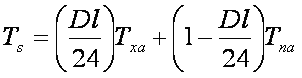
where Dl is day lighting length (hour).
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: iPhone web sites made easy