In WOFOST, there is the implementation of astronomic routines for deriving variables used in the algorithms of the model.
Here there are the equations used for the calculation of these variables:
Solar declination
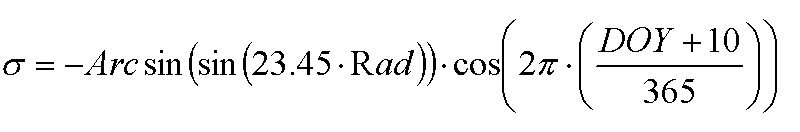
where σ is solar declination at a certain day (radians), Rad is conversion factor from degree to radiant (unitless, 0.0174533) and DOY is day of the year (unitless).
Solar constant
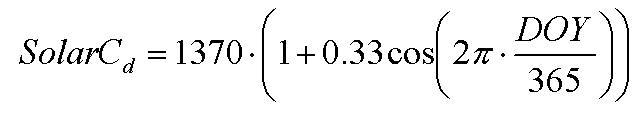
where SolarCd is solar constant at the top of the atmosphere for a certain day (W m-2) and DOY is day of the year (unitless).
Seasonal offset of sine of solar height
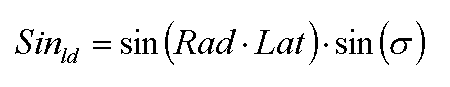
where Sinld is seasonal offset of sine of solar height at a certain day (unitless), Rad is conversion factor from degree to radiant (unitless, 0.0174533), Lat is latitude of the site (degree) and σ is solar declination at a certain day (radians).
Amplitude of sine of solar height
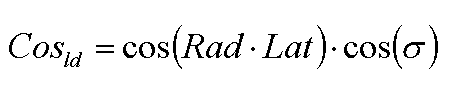
where Cosld is amplitude of sine of solar height at a certain day (unitless), Rad is conversion factor from degree to radiant (unitless, 0.0174533), Lat is latitude of the site (degree) and σ is solar declination at a certain day (radians).
Day length
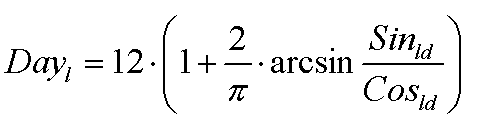
where Dayl is day length (hours), Sinld is seasonal offset of sine of solar height (unitless) and Cosld is amplitude of sine of solar height (unitless).
Integral solar height
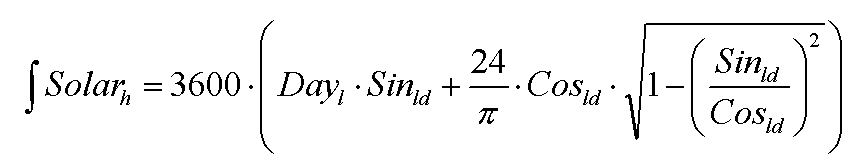
where Solarh is solar height (s), Dayl is day length (hours), Sinld is seasonal offset of sine of solar height (unitless) and Cosld is amplitude of sine of solar height (unitless).
Integral effective solar height
The integral of the effective solar height takes the effect of the daily course in atmospheric transmission into account. Due to haze in the morning and clouds in the afternoon, transmission is lower near the margins of the day. Besides that, path length of solar radiation in the atmosphere is longer (Spitters et al., 1986). The modified integral can be calculated as:
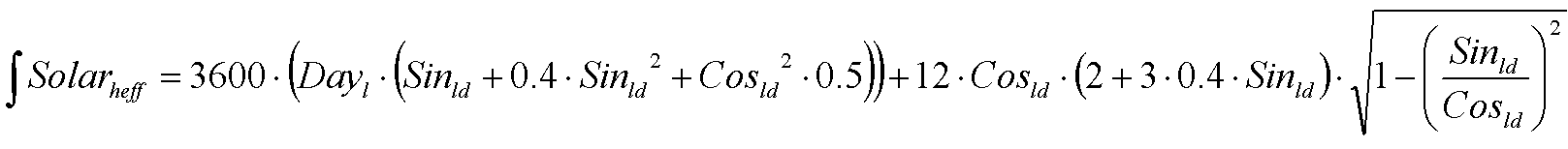
where Solarheff is effective solar height (s), Dayl is day length (hours), Sinld is seasonal offset of sine of solar height (unitless) and Cosld is amplitude of sine of solar height (unitless).
Extraterrestrial radiation
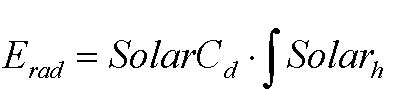
where Erad is extraterrestrial solar radiation at a certain day (W m-2), SolarCd is solar constant at the top of the atmosphere for a certain day (W m-2) and Solarh is solar height (s).
Atmospheric transmissivity
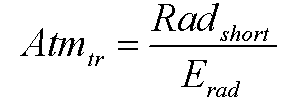
where Atmtr is atmospheric transmissivity (unitless), Radshort is shortwave net radiation (W m-2) and Erad is extraterrestrial solar radiation at a certain day (W m-2).
Fraction of diffuse radiation
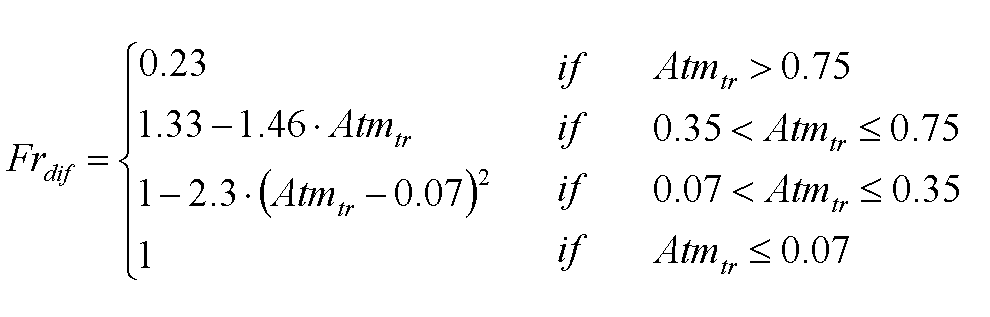
where Frdif is the fraction of daily diffuse radiation (unitless) and Atmtr is atmospheric transmissivity (unitless).
Diffuse radiation perpendicular to direction of light
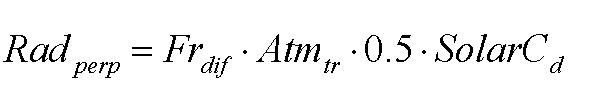
where Radperp is diffuse irradiation perpendicular to the direction of light (W m-2), Atmtr is atmospheric transmissivity (unitless) and SolarCd is solar constant at the top of the atmosphere for a certain day (W m-2).
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Free CHM Help documentation generator