Leaves death can be caused by self shading or by senescence.
Self shading
The relative death rate due to self-shading increases linearly from zero at a certain, critical leaf area index, to its maximum value at twice this critical leaf area index. Typical values for the maximum relative death rate and the critical LAI are fixed into 0.03 d-1 and 4 ha ha-1, respectively.
Firstly, the extinction coefficient for the diffuse radiation flux in function of development stage is calculated via an AFGEN table (see also topic Solar radiation reflection and extinction). Then, a critical leaf area index value is calculated, using this extinction coefficient with the equation:
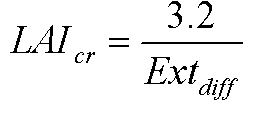
where LAIcr is critical leaf area index (m2 m-2), and Extdiff is the extinction coefficient of diffused light (unitless).
Then, this value of LAIcr is used for calculating the potential death rate of leaves due to high values of LAI with the equations:
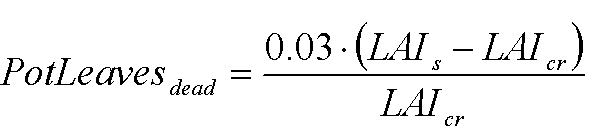
where PotLeavesdead is potential death rate of leaves due to high LAI (Kg ha-1 d-1), LAIs is total leaf area index at time step s (m2 m-2) and LAIcr is critical leaf area index (m2 m-2).
Then the weight of leaves that have died during current time step can be calculated with the following equation:
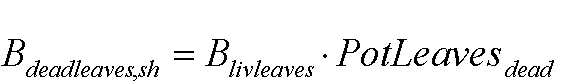
where Bdeadleaves,sh is the weight of leaves that have died during current time step due to self shading (kg ha-1), Blivleaves is daily rate of dry weight of living leaves (Kg ha-1 d-1) and PotLeavesdead is potential death rate of leaves due to self shading (Kg ha-1 d-1).
Senescence
Life span (i.e. physiologic ageing) is crop specific and is defined as the maximum time in days a leaf can live at a constant temperature of 35°C. The physiologic ageing factor per time step can be calculated as:
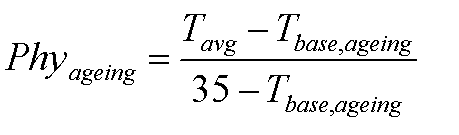
where Phyageing is the rate of physiologic ageing factor for leaf age increase (unitless), Tavg is average daily air temperature (°C) and Tbase,ageing is lower threshold temperature for physiologic ageing (°C, to be provided by the user).
Then, the integration of the rate of physiologic ageing factor over time yields the physiologic age:
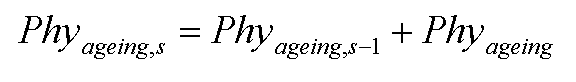
where Phyageing,s is physiologic age at time step s, Phyageing,s-1 is physiologic age at time step s-1 and Phyageing is the rate of physiologic ageing factor for leaf age increase (unitless).
Leaves may attain the age defined by the crop specific life span and they can not exceed it. Leaf age classes are checked; the first class younger than the defined life span become the oldest class. Note that death of old leaves takes place after ageing, being the result of the daily shifting from one leaf class to the next (Johnson & Thornley, 1983). In this way, life time of leaves is the maximum number of days that a leaf class contributes to the LAI and to photosynthesis.
Finally, for obtaining the total rate of leaves dead biomass , this equation is applied:
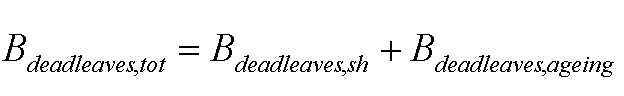
where Bdeadleaves,tot is the total rate of leaves dead biomass (Kg ha-1), Bdeadleaves,sh is the weight of leaves that have died during current time step due to self shading (kg ha-1) and Bdeadleaves,ageing is is the weight of leaves that have died during current time step due to senescence (kg ha-1).
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Free help authoring environment